| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||
| 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
| 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 |
| 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
- blockchain
- NFT
- Ethereum
- 제어의역전
- web3.js
- JavaScript
- geth
- 트랜잭션
- erc
- github
- ERC20
- erc721
- 블록체인
- server
- ethers
- 네트워크
- 이더리움
- Programming
- solidity
- tcp
- ERC165
- web
- Python
- web3
- truffle
- 스마트 컨트랙트
- git
- 솔리디티
- Docker
- MySQL
- Today
- Total
멍개의 연구소
[블록체인] 파이썬으로 블록체인을 구현해보자 - 2 (Consensus) 본문
지난 시간에 이어 이번에는 블록체인의 Consensus문제에 대해서 알아보겠습니다.
2022.08.27 - [블록체인] - [블록체인] 파이썬으로 블록체인을 구현해보자 - 1 (블록 생성, 트랜젝션 생성, POW, 마이닝)
[블록체인] 파이썬으로 블록체인을 구현해보자 - 1 (블록생성, 트랜젝션 생성, POW, 마이닝)
파이썬을 이용하여 블록체인을 구현해보도록 하겠습니다. ● 블록체인 구현 블록체인을 구현해보도록 하겠습니다. 1. 블록체인 기본구조 파일명: blockchain.py class Blockchain(object): def __init__(self): se
meongae.tistory.com
Consensus 문제란 분산화된 환경에서 노드들의 체인이 같아야 하는데 이 문제를 Consensus 문제라고 합니다.
우리는 분산화된 환경에서 트랜젝션과 마이닝된 블록을 가지고 있습니다.
· 새로운 노드 등록
Consensus 알고리즘을 구현하기 전에 이웃노드에 대해서 아는 방법이 있어야 합니다. 네트워크 상 노드들은 다른 노드들의 정보를 유지해야 합니다. endpoint를 이용하여 이를 구현합니다. 다른 노드들을 유지할 수 있도록 API를 추가합니다.
1. /nodes/register : 새로운 노드를 등록.
2. /nodes/resolve : 올바른 체인을 가지고 있는지 확인.
▷ blockchain.py -> Blockchain
. . .
from urllib.parse import urlparse
. . .
class Blockchain(object):
def __init__(self):
...
self.nodes = set()
...
def register_node(self, address):
parsed_url = urlparse(address)
self.nodes.add(parsed_url.netloc)기존의 Blockchain 클래스에서 앞의 코드를 추가합니다. 우리는 노드 정보를 set() 타입으로 저장합니다. 즉 노드의 URL의 중복을 허용하지 않게 됩니다.
...
import requests
class Blockchain(object)
...
def valid_chain(self, chain):
last_block = chain[0]
current_index = 1
while current_index < len(chain):
block = chain[current_index]
print(f'{last_block}')
print(f'{block}')
print("\n-----------\n")
# Check that the hash of the block is correct
if block['previous_hash'] != self.hash(last_block):
return False
# Check that the Proof of Work is correct
if not self.valid_proof(last_block['proof'], block['proof']):
return False
last_block = block
current_index += 1
return True
def resolve_conflicts(self):
neighbours = self.nodes
new_chain = None
max_length = len(self.chain)
for node in neighbours:
response = requests.get('http://{%s}/chain'%(node))
if response.status_code == 200:
length = response.json()['length']
chain = response.json()['chain']
if length > max_length and self.valid_chain(chain):
max_length = length
new_chain = chain
if new_chain:
self.chain = new_chain
return True
return Falsevalid_chain()은 각각의 블록과 증명의 유효성 검사를 합니다.
resolve_conflict()는 다른 네트워크에 있는 노드들을 검사하여 길이간 긴 체인으로 교체합니다.
다음으로 서버 쪽에서 2개의 API를 추가합니다.
▷ /nodes/register : 노드 등록
app.route('/nodes/register', methods=['POST'])
def register_nodes():
values = request.get_json()
nodes = values.get('nodes')
if nodes is None:
return "Error: Please supply a valid list of nodes", 400
for node in nodes:
blockchain.register_node(node)
response = {
'message': 'New nodes have been added',
'total_nodes': list(blockchain.nodes),
}
return jsonify(response), 201▷ /nodes/resolve : 체인 확인
@app.route('/nodes/resolve', methods=['GET'])
def consensus():
replaced = blockchain.resolve_conflicts()
if replaced:
response = {
'message': 'Our chain was replaced',
'new_chain': blockchain.chain
}
else:
response = {
'message': 'Our chain is authoritative',
'chain': blockchain.chain
}
return jsonify(response), 200해당 API는 네트워크상에 존재하는 노드들의 체인을 똑같이 유지시켜줍니다.
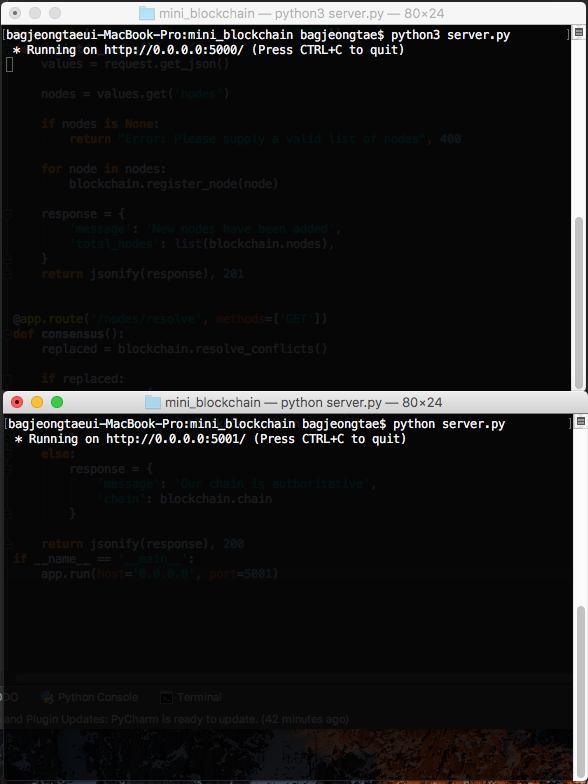
이제 포트 번호로 다른 노드로 가정하고 2개의 서버를 띄웠습니다. 각 서버는 서로 다른 노드를 의미합니다.
· 노드 등록
5000번 포트 노드에게 5001번 포트 노드를 등록합니다.
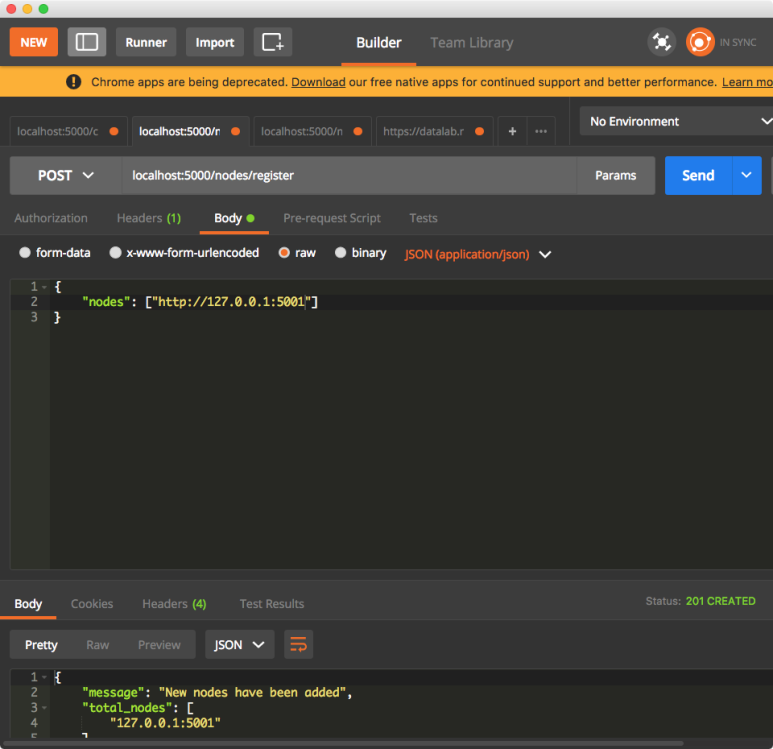
그럼 이제 5001번 포트 노드에게 트랜젝션을 만든 후 mine을 통해 블록을 생성해보겠습니다. 그리고 5000번 포트에서 체인을 확인해보겠습니다.
· 마이닝
5000번에게 5001번 노드를 등록했으니 5001번에서 블록을 생성해봅니다.
마이닝을 하기 전에 트랜젝션을 발생시킵니다.
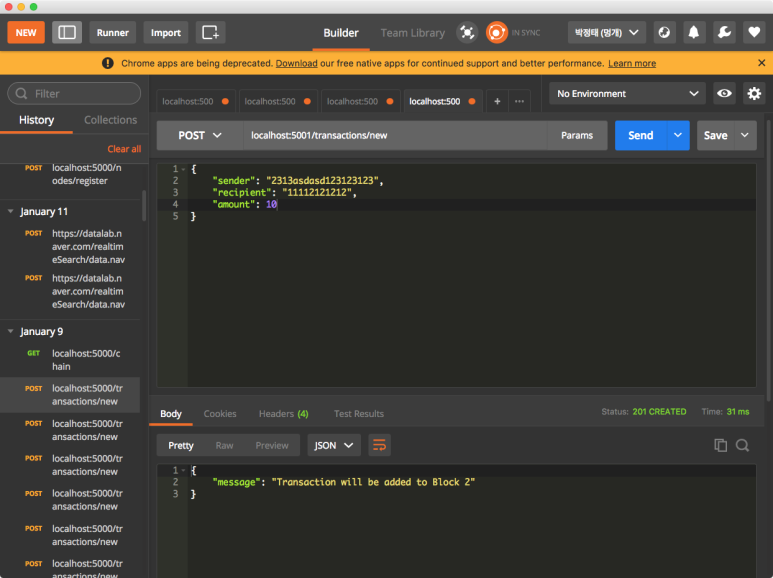
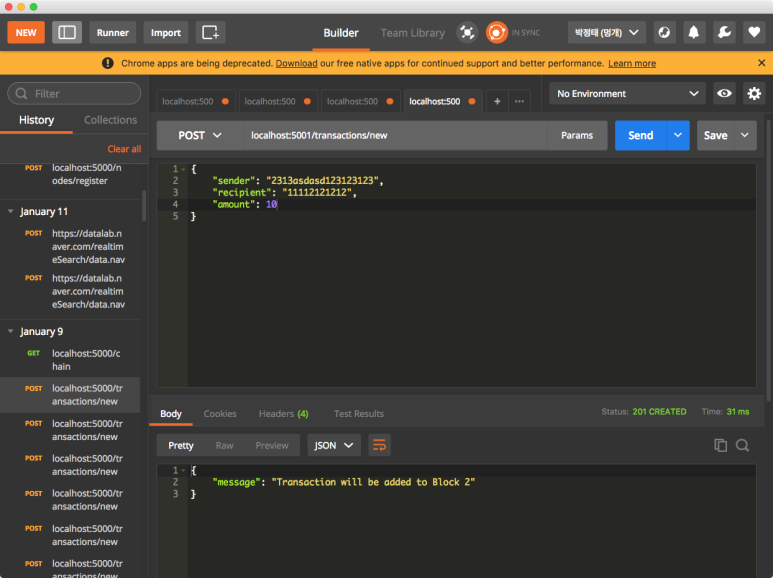
마이닝을 통해 발생된 트랜젝션을 블록으로 만들어 체인에 붙여줍니다.
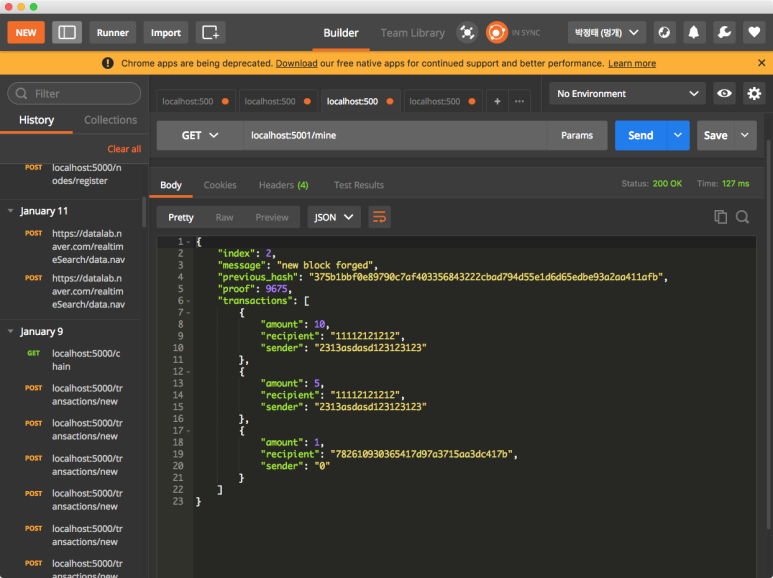
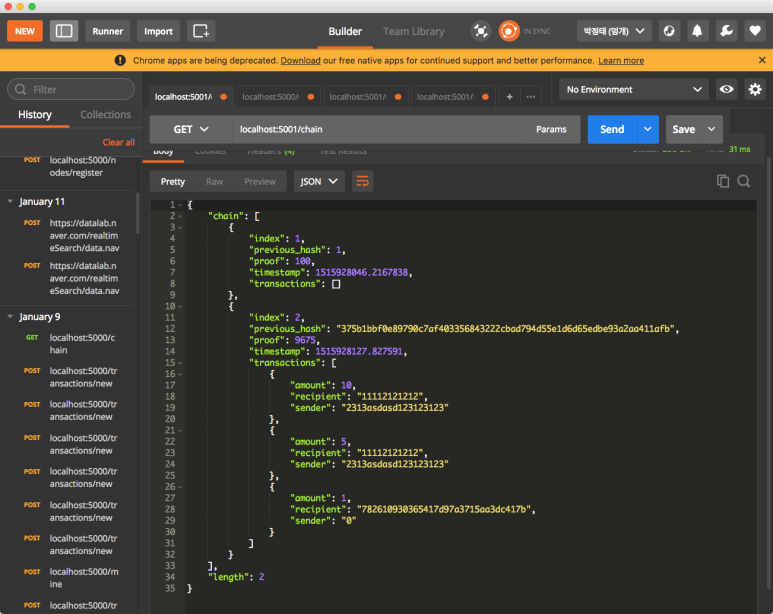
5001번 포트 노드에서 마이닝을 통하여 발생된 트랜젝션이 블록으로 잘 만들어져 체인에 붙어있습니다.
자 그럼 5000번 포트 노드에서 해당 노드의 정보와 동기화시켜보겠습니다.
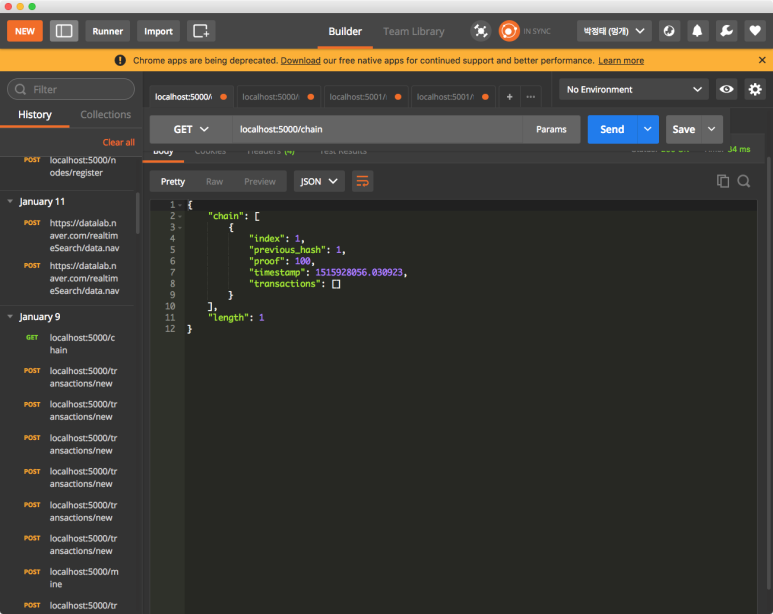
동기화하기 전 모습입니다.
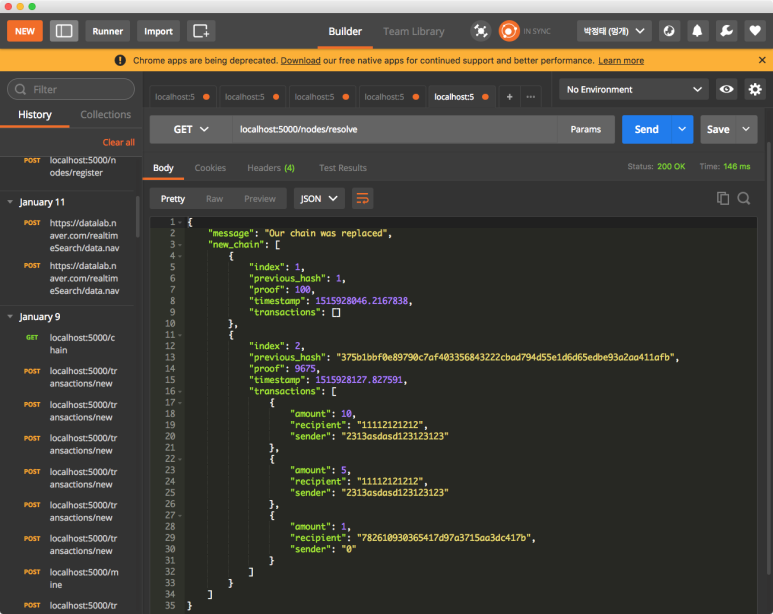
/nodes/resolve API를 호출하여 등록된 노드 중에서 가장 긴 체인을 찾아 해당 체인으로 노드의 체인을 교체합니다.
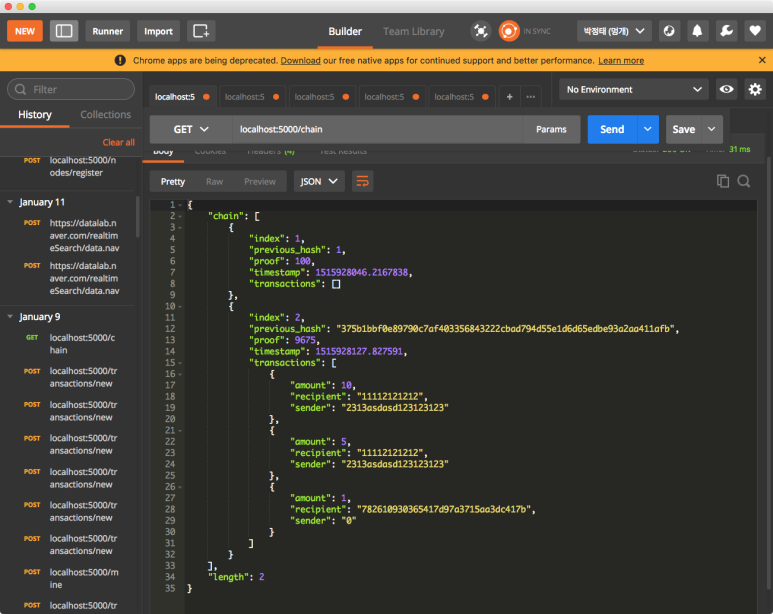
5000번 포트 노드의 체인이 5001번 포트 노드 체인과 동일하게 바뀌었음을 확인할 수 있습니다.
해당 포스팅은 다음 글을 번역한 내용이며, 일부 개인적인 생각을 포함한 곳이 있습니다.
https://hackernoon.com/learn-blockchains-by-building-one-117428612f46
또한 다음 코드를 일부 참고했습니다.
'블록체인' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [hyperledge fabric] fabric 기반 블록체인 기술을 익히는데 필요한 용어 (0) | 2022.08.27 |
|---|---|
| [ethereum] Token, ICO 1편 - 동작과정 (0) | 2022.08.27 |
| [ethereum] 토큰 발행/ICO 까지 개념, 테스트 완료 (0) | 2022.08.27 |
| [블록체인] 파이썬으로 블록체인을 구현해보자 - 1 (블록생성, 트랜젝션 생성, POW, 마이닝) (2) | 2022.08.27 |
| [가상화페] 화폐, 가상화폐 (1) | 2022.08.27 |





